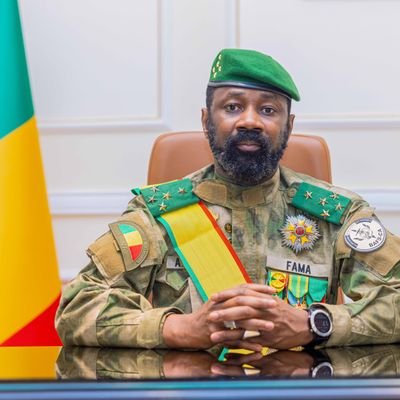
Général Assimi Goïta, Président de la Transition malienne-Bilan 2024
Général Assimi Goïta, Président de la Transition malienne-Bilan 2024
Le 31 décembre 2024, le Général Assimi Goïta, Président de la Transition malienne, s’est adressé à la nation, appelant à une unité renforcée autour des idéaux de développement et de paix pour l’année 2025. Il a souligné les progrès réalisés en 2024 et a défini les priorités pour l’année à venir, mettant l’accent sur la souveraineté, la sécurité, l’économie et la culture.
Bilan de l’année 2024
Le Président Goïta a rappelé les avancées significatives en matière de souveraineté nationale, obtenues grâce à des réformes institutionnelles et à l’engagement du peuple malien. Il a également évoqué les défis rencontrés, notamment les inondations qui ont touché de nombreuses communautés, et a salué la résilience des populations face à ces épreuves.
Priorités pour 2025
Sécurité : Les Forces armées maliennes (FAMa) intensifieront leurs opérations sur l’ensemble du territoire, avec une attention particulière à la région de Kidal, où des opérations spéciales ont déjà permis de neutraliser des chefs terroristes. Le Président a promis une amélioration des capacités d’anticipation et le redéploiement des forces dans les zones reconquises.
Économie : L’État a renforcé son contrôle sur des secteurs clés, devenant actionnaire majoritaire dans la Banque nationale de développement agricole (BNDA) et Moov Malitel. Des investissements significatifs, notamment l’ouverture de la mine de lithium de Goulamina, devraient générer des recettes substantielles, contribuant ainsi à la relance économique.
Énergie : Face à la crise énergétique, des projets de centrales solaires à Sanankoroba, Safo et Tiakadougou Dialakoro ont été lancés pour diversifier les sources d’énergie et améliorer la fourniture électrique.
Lutte contre la corruption : Le Président a réaffirmé son engagement à combattre la corruption et l’enrichissement illicite, s’appuyant sur les rapports du Bureau du Vérificateur général et de l’Office central de lutte contre l’enrichissement illicite pour initier des actions concrètes.
Culture : L’année 2025 a été déclarée “Année de la culture”, visant à revitaliser les valeurs traditionnelles, promouvoir les talents artistiques et renforcer l’identité culturelle nationale. Un programme national d’éducation aux valeurs, lancé en avril 2024, entend inculquer le patriotisme et la cohésion sociale à la jeunesse malienne.
Appel à l’unité nationale
Le Général Goïta a conclu son discours en appelant à l’union sacrée pour réussir les réformes engagées et construire un Mali nouveau. Il a insisté sur la nécessité d’une collaboration étroite entre les différentes composantes de la société pour garantir un avenir de stabilité, de prospérité et de souveraineté pour le pays.
Ce discours de fin d’année réaffirme la détermination des autorités de la Transition à œuvrer pour un Mali uni, sécurisé et prospère, en plaçant le développement et la paix au cœur de leurs priorités pour 2025.